India has achieved a significant milestone in lunar exploration by successfully landing a craft on the Moon’s south pole, making it the first nation to accomplish this feat.
The achievement marks a pivotal moment in the global space race, captivating both established space powers and emerging participants.
This achievement came shortly after Russia’s Luna-25 probe crash-landed on the Moon.
India’s Chandrayaan-3 mission, a continuation of its lunar exploration endeavours, follows a successful lunar orbit insertion in 2008 and a failed landing attempt in 2019.
Launched in mid-July, the craft meticulously built up speed through Earth’s orbits to facilitate its lunar journey.
The triumphant landing paves the way for a solar-powered rover to explore the lesser-charted southern lunar pole, relaying data back to Earth during its two-week operational span.
Consequently, this accomplishment aligns with India’s trend of ambitious and cost-effective space ventures, including its Mars orbiter mission in 2014 and a forthcoming crewed mission.
–Russia’s Roulette–
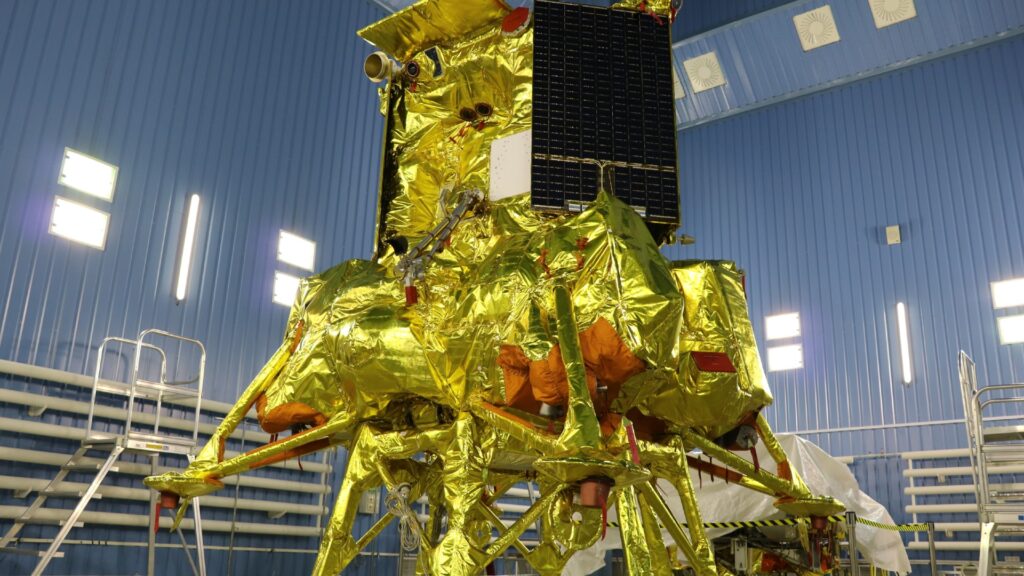
Russia’s recent lunar initiative, Luna-25, embarked on its first lunar mission in nearly five decades.
Despite successfully reaching lunar orbit, the lander met an unfortunate end due to a collision with the Moon’s surface.
Russia’s lunar pursuits aim to recapture the glory of the Soviet-era Luna program. This is a critical move in light of internal financial struggles and corruption issues.

-China’s Chance-
China, a critical player in the space realm, has substantial plans to send a crewed mission to the Moon by 2030 and establish a lunar base.
In addition to significant investments in its space program, China has rapidly progressed, achieving human spaceflight, Mars and Moon rover landings, and sample return missions.
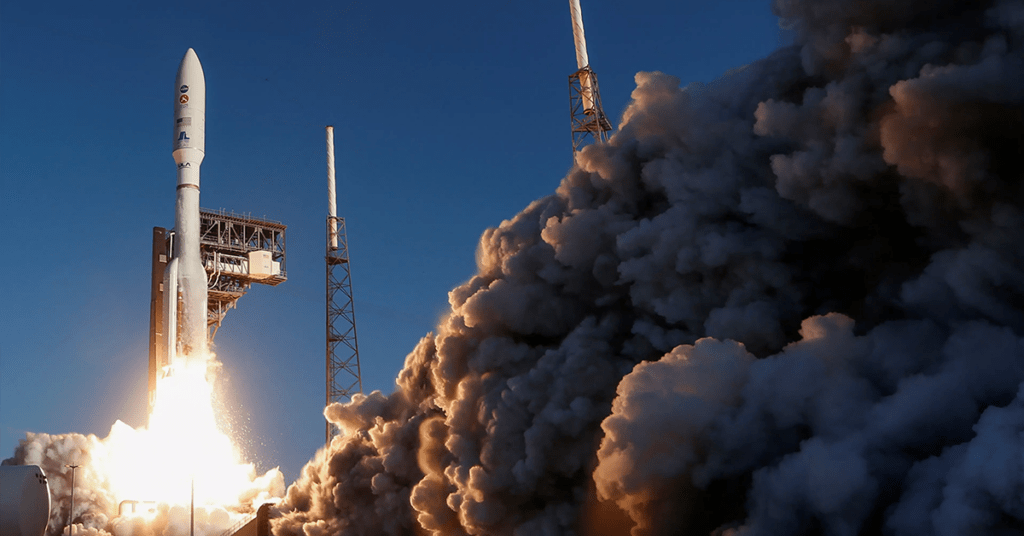

NASA’s Artemis program, set to return humans to the Moon by 2025, is a centrepiece of lunar exploration.
Intending to establish a sustained lunar presence, NASA’s mission trajectory involves increasingly intricate missions to pave the way for Mars expeditions.
The Artemis program involves collaborations with private entities, like Musk-owned SpaceX, which secured the contract for a lunar landing system.
In essence, India’s recent lunar landing, along with Russia’s and China’s pursuits, reflects the escalating momentum in lunar exploration.
As nations and private companies vie for lunar achievements, each success and setback contributes to the unfolding story of man in space.