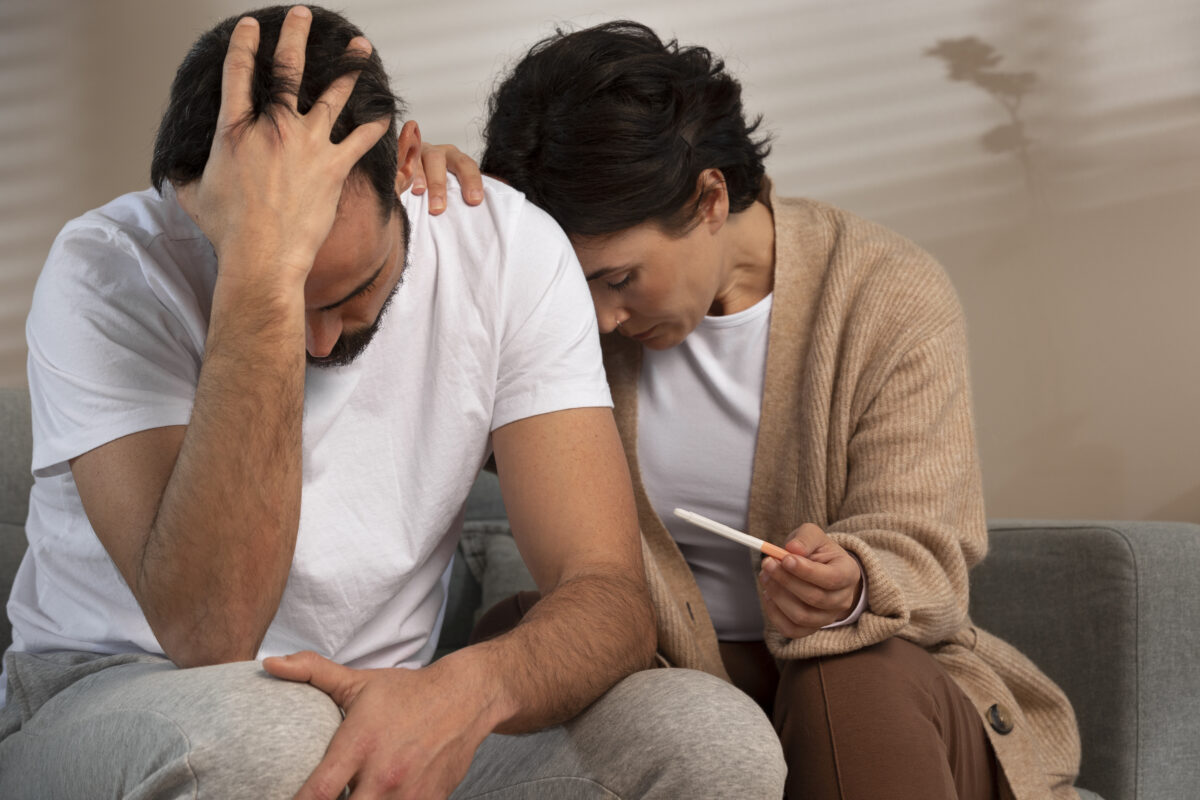
Infertility is a growing concern among couples worldwide, affecting both men and women.
On the Morning Cafe show at TV47, Dr. Stephen K. Ngigi, a family medicine specialist, explained causes and remedies.

Infertility is defined as the inability of a couple to conceive.
Especially after engaging in unprotected sexual intercourse for more than a year without using any family planning methods.
While infertility is often seen as a female issue, Dr. Ngigi emphasizes the importance of considering male factors as well.
Causes of Infertility
Infertility can be caused by a range of factors, classified into congenital (present from birth) and acquired (developed later in life) causes.
Congenital Causes
Some women may be born with conditions such as polycystic ovarian disease, abnormalities of the uterus, or underdeveloped ovaries, which can impact their ability to conceive.
Some men may have undescended testes (cryptorchidism) or other reproductive organ deformities that affect sperm production and quality.
Sexually transmitted diseases
Sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia and gonorrhea can lead to chronic pelvic inflammatory disease, causing blockages in the fallopian tubes and preventing fertilization.
In some cases, tuberculosis can affect the ovaries in women or male reproductive organs, leading to fertility problems.
Non-cancerous growths in the uterus, known as fibroids, can interfere with implantation and pregnancy, causing recurrent pregnancy loss.
Conditions such as hypothyroidism (goiter), diabetes, and metabolic syndrome can disrupt reproductive function
Alcohol and old age
Excessive consumption of alcohol, smoking, and drug use can affect sperm production and quality in men, leading to low sperm count or poor sperm motility.
Women are most fertile between the ages of 21 and 35. After 35, fertility declines, increasing the risk of pregnancy complications.
Prevention of Infertility
Although some causes of infertility are beyond human control, many cases can be prevented by adopting a healthy lifestyle.
Avoiding sexually transmitted infections by practicing safe sex can reduce the risk of infertility.
Maintaining a balanced diet and an active lifestyle can help regulate hormonal balance and prevent obesity-related infertility.
Early diagnosis and treatment of conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and infections can prevent complications that lead to infertility.
Reducing alcohol intake, quitting smoking, and avoiding drug abuse can significantly improve reproductive health.
Remedies for Infertility
For couples struggling with infertility, several treatment options are available depending on the underlying cause.
Fertility treatments such as hormone therapy, antibiotics for infections, and medication to stimulate ovulation can help restore fertility.
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove fibroids, correct reproductive organ abnormalities, or unblock fallopian tubes.
Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART):
Procedures such as in-vitro fertilization (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI) can assist couples in achieving pregnancy.
Improving diet, reducing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight can enhance fertility.
Conclusion
By understanding the factors that contribute to infertility and taking preventive measures, couples can improve their chances of conception.
Seeking professional medical advice and adopting a healthy lifestyle can play a crucial role in overcoming infertility challenges.












